Cardiac arrest tops the list of potential problems with taking this commonly used drug.
As if we needed another reason to question taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, a new study has concluded that taking these drugs increases the risk of cardiac arrest by a whopping 31 percent. A cardiac arrest is a serious medical emergency as the heart stops pumping blood throughout the body.
The study was based on the analysis of 28,947 cardiac patients in Denmark, and was published in the European Heart Journal.
“Our findings support the accumulating evidence of an unfavourable cardiovascular risk profile associated with use of the non-selective NSAIDs. This calls for special awareness in order to balance risks against benefits in treatment with NSAIDs,” the researchers concluded.
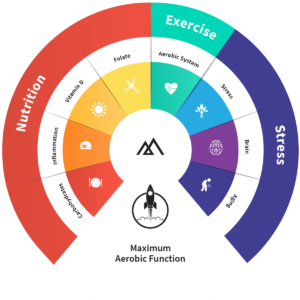
Despite this and other warnings, NSAIDs remain the most commonly used and abused drugs, typically for pain. They are particularly dangerous because they are widely available over the counter and because their use is typically considered benign both by consumers and medical professionals. Thirty-three million Americans regularly use NSAIDs, with millions others worldwide. In fact, many people, especially athletes, include them in their daily routines the same way they do dietary supplements.
But these drugs are far from benign. There are many common problems and side-effects associated with their use. In addition to increased cardiac risk, consider these other issues associated with the use of NSAIDs:
- In addition to cardiac arrest, NSAIDs are associated with other heart issues such as increased risk of atrial fibrillation or heart flutter.
- These drugs may delay healing.
- NSAIDs disrupt the body’s own anti-inflammatory system. While reducing certain molecules responsible for inflammation, natural anti-inflammatory molecules also are impaired.
- About 16,500 people annually die due to NSAIDs use. The culprit is usually ulcer-related complications associated with the drug’s continued use.
- Intestinal problems, including bleeding, occur in almost everyone taking NSAIDs (even if it’s not noticeable). This can lead to anemia and fatigue.
- Muscle dysfunction, contributing to physical aches and pains, and injuries is often prevalent among NSAIDs users.
- NSAIDs can reduce the body’s ability to repair joint and bone stress.
- Increased risk of kidney damage, especially when you’re dehydrated, can result from taking NSAIDs.
- NSAIDs can disturb sleep.
- Immune system stress often accompanies NSAIDs use.
For certain, no injury or inflammatory condition is caused by a drug deficiency. Before reaching for a magic pill to cure your pain, consider the cause of the problem and seek out more natural choices for remedies, especially balancing fat and eating certain foods.